Mutual Funds refers to the corpus of money amassed by various investors who desire to save their money and earn high via their investment. The accumulated money is then invested in different asset categories like debt funds, liquid assets etc.
Each shareholder, therefore, participates proportionally in the gains or losses of the fund. The profits earned and losses incurred over a period of time have to be shared in a similar fashion among the investors in consonance with their proportion of contribution in the corpus.
Mutual Funds are registered with SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India) that regulates security markets before the collection of the funds from the investors.
Investing in a Mutual Funds is not a big task, in fact, it is as simple as online trading of stocks or bonds and investors can sell out their shares whenever they wish to.
Types of Mutual Funds in India
A wide range of mutual funds in India is classified on the basis of investment objective, asset class, and structure.
Let’s have a look at different types of mutual funds:
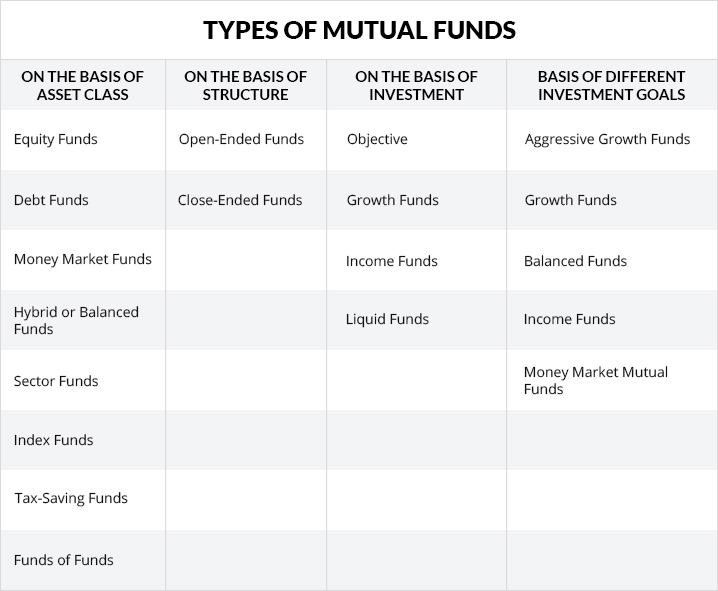
Types of Mutual Funds Based on the Basis of Asset Class:
Equity Funds –
Equity funds are mutual funds which invest principally in equity stocks or shares of the company. Equity funds are highly risky but at the same time, they have a tendency to manifest higher returns in the long term. They are also known as stock funds.
Debt Funds –
Debt funds are mutual funds which usually invest in the debts such as government securities, government bonds, corporate bonds and fixed income assets etc. Debt funds are likely to more stable.Because of their ability to provide fixed returns, they are referred to as a safe investment tool.
Money Market Funds –
A money market refers to the mutual funds that are invested in liquid instruments or short-term investments like CPs, T-Bills etc. These mutual funds are highly liquid and one can invest money in money market funds for a duration of a day or two even. They are safe investment choice with instant yet moderate return on the investment, a perfect selection for investors with abundant funds.
Hybrid or Balanced Funds –
A Balanced or hybrid fund is a blend of equity and debt funds which offers a one-stop investment mix by investing an equal amount in equity and debt funds to maintain a perfect balance between risk levels and returns in the investment, fair enough for maximum diversification and assured return.
Recommended: Registrar and Transfer Agents (RTA) Benefits To Mutual Fund House
Sector Funds –
Mutual funds which invest in a particular sector or division of the market are known to be sector-specific funds. For instance, health care companies like Pfizer, United-Healthcare, Cigna Corp, Abbott Laboratories etc invest in health sector mutual fund, such as Vanguard Health Care (VGHCX) or T. Rowe Price Health Sciences (PRHSX), for broad exposure to the healthcare industry.
Returns and risks on an investment are completely based on the performance of that specific sector. As the portfolio of such mutual funds encompasses investment in a specific type of sector, they offer lesser diversification and are prone to high risks.
Index Funds –
The index fund is a kind of investment which is made to match the working of a financial market index, such as the Standard & Poor’s 500 Index (S&P 500). These funds are investment tools that represent specific index on the exchange with the purpose to track the returns and the movement of the index, viz. purchasing shares from the BSE Sensex. Benefits include broader exposure to the market, less operating cost and low portfolio turnover.
Tax-Saving Funds –
These funds make investment majorly in the equity shares. Tax-saving funds make an investor eligible to claim tax deductions under the Income Tax Act. The risk factor involved in these funds is usually high but at the same time it accompanies higher returns if the funds perform well.
Funds of Funds –
A fund of funds (FOF) – also known as a multi-manager investment – is a mutual fund scheme that invests in other schemes of mutual funds and the returns are based on the overall performance of the target funds.
Types of Mutual Funds Based on Structure:
Open-Ended Funds –
Open-Ended Funds are investment tools which deal with units that are purchased or redeemed throughout the year. Such purchases or redemptions are done at the ongoing Net Asset Value (NAV). These funds offer high liquidity to the investors which interprets that an investor may exit anytime and they get money at the current NAV, which is published by the mutual fund houses daily, that’s is why it is highly preferable as well.
Close-Ended Funds –
Close-Ended mutual funds investment tools deal with units that are purchasable only at the initial period. The units are redeemable only on a specific maturity date which means investors can neither enter nor exit from the scheme till the term of the scheme ends. To maintain liquidity, these schemes are listed on the stock exchange for trading purposes.
Mutual Funds Classified on the Based of Investment Objective –
Growth Funds –
A growth fund is an assorted portfolio of equity stocks of companies expected to grow revenue as its primary motive is to provide capital appreciation. These funds are risky but yet ideal for investors who prefer long-term investments.
Income Funds –
Income Funds are investment instrument via which money gets invested in fixed income instruments such as high dividend generating stocks, government securities, certificate of deposits, corporate bonds, money market Instruments and debentures. It mainly focuses on generating a steady income for the investors and serving them with maximum capital protection.
Liquid Funds –
Liquid funds are simply debt mutual funds that invest your money in very short-term market instruments like CPs, T-Bills, government securities etc. The primary focus is to provide liquidity to investors. These schemes have a short maturity period, holds least risk factor and moderate returns on investment, perfect option for investors who prefer short-term investments.
Different Mutual Funds on the Basis of Mutual Fund Investment Goals:
Mutual fund manager sets goals for different mutual fund investments. Every mutual fund has its own primary and other goals.
So, on the basis of these different objectives, mutual funds are divided into 5 categories, which are as follows:
1. Aggressive Growth Funds –
Aggressive growth is a mutual fund investment tool that seeks huge capital profits from aggressive growth stocks (Stocks of companies with the ability to grow at a faster pace as compared to the overall stock market).
Aggressive growth funds have higher chances of sudden growth and so the risk factor involved is also very high. Investing in these funds is an ideal option for the investors who are willing to invest their money for a time period of five years and their investment objective is to fetch high returns in the long run.
The investors whose objective revolve around conserving capital and can’t afford to lose the value of their investment , should not invest in aggressive growth funds as the funds with instant price appreciation ability lose their value promptly during the recession in the economy.
2. Growth Funds –
A mutual fund that invests in growth stocks (an emerging company) to fetch maximum capital appreciation is a growth mutual fund. The fund manager would opt for a growth stock, which uses the growth for yielding profits and not for paying the dividends. Usually holding onto growth funds proves profitable for the investor(s). The option is ideal for long -term investors who wish to earn huge profits.
3. Balanced Funds –
A balanced fund is a blend of the income and growth funds with a mixture of goals to achieve. Balanced funds are best for investors who desire a fusion of safety, income, and modest capital appreciation. The stability range of ‘Balanced funds’ lies between low to moderate, however, its potential for growth and current income is moderate.
4. Income Funds –
Income funds ensure a steady income for investors by investing in high dividend generating stocks, government securities, certificate of deposits, corporate bonds, money market Instruments and debentures. These funds are perfect for the investors who are retired, as they will have a regular supply of dividends. It is a stable investment tool with moderate risk factor because the changes in the rate of interest and inflation affect the prices of income share funds and bonds also.
5. Money Market Mutual Funds –
A money market fund is a mutual fund that invests solely in highly liquid instruments like cash, cash equivalent securities, and high credit rating debt-based securities coupled with a short-term maturity i.e. less than 13 months. As a result, it offers higher liquidity at a very low-risk factor which further enables investors to alter and reformulate their investments strategies.
How to Make a Fund Selection?
Factors like financial goals, risk-bearing capacity, time period and capital affect the investment decisions so for the right selection of mutual fund investment instrument, a thorough evaluation of your fiscal goals, time frame and risk threshold should be done. In this way, you can select the most preferable option for you.
The following tips will help you formulate your investment strategies:
Diversification – An Important key
If you put all the eggs in one basket, the risk factor elevates while if you diversify your capital in different mutual fund investment tools, the risk involved is stabilized because the risk in a fund which is not yielding great returns, tends to be nullified against other investment instruments.
Inflation – A Considerable Factor
One needs to keep the inflation factor also in his/her mind while choosing for a mutual fund to invest in. If the inflation rate is lower then the rate of return then it seems a good idea for the investment but if an inflation rate tends to spread its wings wider in the coming future, you will end up with losses.
For example, if the rate of return is 8% but the inflation rate is 9 %, you will have a 1% loss with such an investment.
Patience – One of the key
Patience is one of the keys to harvesting good returns in the unpredictable & volatile market of mutual funds. One should keep patience and should not withdraw instantly if the funds fall short of its value. Collapsing funds can perform great later. So one should be patient to analyse the situation thoroughly and to let their funds recover itself. A Person with patience can opt for long-term investment.
Age – A Role Player
Age plays an important role while formulating an investment strategy as young investors have ample time to invest in long term investment tools which can yield them high returns over a period of time while people at retiring edge should go for short-term and safe investments like money market fund or bonds.
Risk Threshold – A Major Determinant
Risk Threshold is the limit of risk an investor is willing to bear with his/her invested money. If your risk tolerance is low then you must invest in liquid funds or ultra short-duration funds while if it is high you can choose arbitrage funds, small-cap funds etc.
Time Horizon – An Inevitable Element
Time horizon means the time period for which you wish to keep your money invested in a mutual fund. It can be either as short as a day or as long as more than 5 years. Different fund categories work best for different time horizons. For instance, one must go for Equity funds if the time horizon exceeds 5 years. In the same way, if the time horizon is between one day to three months then liquid funds are the best choice.
Mutual Funds Benefits – Most obvious
The purpose of investing in mutual funds vary from person to person.Mutual funds serve ample benefits such as professional management, diversification, affordability, liquidity, tax deduction etc. A smart person chooses that mutual fund instrument which offers maximum benefits as per his/her priorities.